Unit 2:
Philosophical Foundations of Education
Philosophy
The word philosophy comes from a combination of two Greek words- “philos” meaning “love” and “sophi” meaning “wisdom.” Thus, philosophy means the love of wisdom. Philosophy is a logical inquiry into the nature of reality. It is systematic enquiry about the ultimate reality of the universe. It is an unceasing effort to discover the general truth that lies behind the particular facts, to discern also the reality that lies behind the appearance. Philosophy is persistent attempt to gain insight into the nature of the world and of ourselves by means of systematic reflections”.
Philosophy and Education
Philosophy and education are two sides of a coin. Philosophy determines the real destination towards which education has to go. Philosophy determines the various aspects of education like Aims, Curriculum, Teaching strategies, assessment and administration and discipline. Great Philosophers have been great educationists also describe, Education is the dynamic side of philosophy.
Objectives of Studying Educational Philosophy
· To find out the solution for various educational issues.
· The purpose of studying educational philosophy is to make education according to the need based life and society.
· To determine the aim of human life, aim of survival.
· To produce better citizen by fostering democratic attitude in behavior.
· To make teaching learning process more effective and attractive according to the need, interest and ability of child.
· To discern the different philosophies and choose any one of them to lead a fruitful life in the society.
· To expand our knowledge and experiences and implement them in the educational practices.
· To bring out all round personality development in child and prepare him to stand\ on his own feet.
· To make education flexible in order to achieve the goals of a country-national integration, international understanding and globalization.
· To develop education as a powerful instrument to bring about social, cultural, political and economical change in society.
Meaning of Realism
The term realism come from the Latin “realists” who is to be really, really real. Realism refers to the things exist whether or not the human mind perceives them. Aristotle was the leading proponent of realism and the first philosopher to develop a systematic theory of logic. In a deeper meaning of realism, it is a philosophy that assumes that there is a real external world that can be recognized.
Values in Realism
· External world is the reality.
· Man will discover reality with the use of science and common sense through education or learning.
· Mind is functioning & is geared towards creativity.
· Reality can be proved by observation, experience, experiment and scientific reasoning.
· Values must be studied to be applied in the actual setting.
Principles of Education
· It is Based on science only.
· Emphasizes on behaviour and experiment
· Child and his present life are the centres of education
· It opposes book learning
· Both the individual and the society are valued
Realism and Aims of Education
· Preparing the child for happy and successful life
· Preparing the child for a real life
· Developing the physical and mental powers of the child
· Developing and training of senses
· Acquainting the child with nature and social environment
· Imparting vocational education
· Character development.
· Realism and Curriculum
· Developed according to Utility and needs
· Subjects concerning day to day activities
· Main subjects are – natural science, physical science, health culture, physical exercise, maths, geography, history, astronomy
Idealism
It is derived from the term ideals. It is a philosophical approach that believes that ideas are the only true and reality worth knowing. The idea of the thing is real and the thing in itself is simple through manifestation of that idea. These ideas are eternal, fixed and unchanging.
Plato is known to be the father of idealism. Truth, knowledge and values are simply the conception of the mind, therefore the mind is the controller and explainer of the phenomenon that we are seeing. Things such as buildings and trees exist but have no existence apart from a mind that conceives them. The external world is in real sense man made. Idealists seek to discover true knowledge rather than create it. In search for truth, beauty and justice i.e. enduring and everlasting, the focus is on conscious reasoning in the mind. Idealism always searches for the truth, it is also commonly known as spiritualism. It seeks to offer an explanation of the man and the universe in-terms of the spirit/mind. The spiritual quality of man distinguishes him from other creatures. Ultimate reality must be understood in-terms of the mind/spirit.
AIMS OF EDUCATION
· Education is supposed to be a process of turning the eye of the soil from darkness into light.
· The role of education is to activate the mind, so that through its own reasoning it can discover knowledge.
· This can be achieved through the Socratic Method.
· Education has to enable the child to realise the soul, recognize his real form and proceed towards self-realization.
· Education should enable children to be able to distinguish right from wrong, being able to follow the right and reject the evil.
· Education should aim at developing the child into a complete being with full physical, intellectual, moral, spiritual, emotional and cultural uplift.
· Education should not only stretch the development of the mind but should also encourage students to focus on all things that are of more lasting value.
· Practical subjects are inferior to academic ones as they not involve the mind.
· Preservation and enrichment of culture is also key in education.
WEAKNESSES OF IDEALISM
· Its notion of a finished and absolute universe waiting to be discovered has hindered progress in science and area of new talents.
· It is impracticable.
· It is also individualistic in nature and neglects socialization of individuals.
Naturalism
Naturalism is a concept that firmly believes that ultimate reality lies in the nature of the matter. Matter is considered to be supreme and mind is the functioning of the brain that is made up of matter. The whole universe is governed by laws of nature and they are changeable.
Chief Characteristics of Naturalism
· Nature alone is the source of all knowledge.
· Mind is subordinate to nature.
· Material world is the real world.
· There is nothing like ‘supernatural’
· All values exist in nature.
· Scientific knowledge is final.
· Values are created in terms of specific needs.
· In the nature order all human being are equal.
· Everything lays in the hands of nature, human being degrades it.
· Man creates societies to meet some of his needs.
Principles of Education according to Naturalism
· Naturalism accords an important place to the educative process.
· Naturalism advocates education in accordance with the nature of the child.
· Naturalism considers natural environment as an important source of education.
· Naturalism gives important to present life of the child.
· Naturalism states that adequate freedom should be given to the child in the education.
· Naturalism has an insignificant place for acquiring knowledge from the books.
Naturalism and Aims of Education
· It is generally says that naturalism has very little to offers regards to the aims of education.
· Developing the child in accordance with the nature.
· Naturalism give permission to children what they want to do.
· It allow children to live in harmony and unity.
· It allow children to live in surrounding environment.
· It give strength to children to fight against struggle.
Naturalism and Curriculum
· Curriculum should be arranged as the attitude, aptitude, interest and needs of the child.
· Curriculum should be prepared in such a way that we can see the overall developmental stages of child.
· Curriculum is based on the nature of the child and his interest.
· It should stresses on science, geometry, English, and all other subjects.
· It should give importance to physical and health science.
· The skill of vocation should develop.
Progressivism
Progressivism is a theory of education that is concerned with “learning by doing “that children learn best when pursuing their own interests and satisfying their own needs. Progressivists believe that people learn best from what they consider most relevant to their lives. Progressivists center curriculum on their needs, experience, interest and abilities of student. Provoke curiosity in students.
Characteristics of Progressivism
· Emphasis on learning by doing
· hands-on projects
· experiential learning
· Integrated curriculum focused on thematic units
· Strong emphasis on problem solving and critical thinking
· Group work and development of social skills
· Understanding and action as the goals of learning as opposed to rote knowledge
· Collaborative and cooperative learning projects
· Education for social responsibility and democracy
Aims of Education
· To develop the personality of an individual through providing a democratic environment in the educational institutions.
· An all-round development of child.
· Cooperative behavior and social participation.
· Education of the whole man, or whole personality, which includes the physical, emotional, social and intellectual aspects of the individual.
Pragmatism
Derived from Greek word ‘pragma’ which means work, practice, action or activity. It is the philosophy of practical experience. The philosophy that encourages people to find processes that work in order to achieve their desired ends. It is a typical American Philosophy practical in appraoch. Pragmatists believe that reality is constantly changing and that we learn best through applying our experiences and thoughts to problems, as they arise.
Basic Principles
· Gives importance to action.
· Gives importance to experience.
· Believes in change.
· No belief in permanent values.
· Gives emphasis on experimentation.
· A practical philosophy.
· A humanistic philosophy.
· Pragmatists believe on present.
· Believe that growth and development takes place through interaction and environment.
· Deep faith in democracy.
· Emphasis on means not on ‘end’.
AIMS OF EDUCATION
· Does not believe in setting predetermined fixed, ultimate and general aims of education.
· The only aim is more and more growth and creation of new values. One can create values through activities and experience.
· Aims of education given by John Dewey in his ‘Democracy and education’:
--Natural development.
--Development of social efficiency.
Essentialism
Essentialists hope that when students leave school, they will possess not only basic skills and an extensive body of knowledge, but also disciplined, practical minds, capable of applying schoolhouse lessons in the real world. (William Bagley)
What is Essentialism?
Essentialism is the educational theory and educational philosophy, whose followers believe that students should learn traditional basic subjects thoroughly. For essentialists, education involves the learning of basic skills, arts and science. After the learning of these skills and subjects students can function as a member of civilized society. Essentialists argue that classrooms should be teacher-oriented. The teacher should serve as an intellectual and moral role model for the students.
Essentialists Beliefs
· Essentialism tries to instill all students with the most basic knowledge, skills and character development.
· Essentialists believe that students should be taught to be a model citizen.
· Essentialists believe that teachers should teach traditional moral values and virtues.
· Essentialists believe in mastery learning.
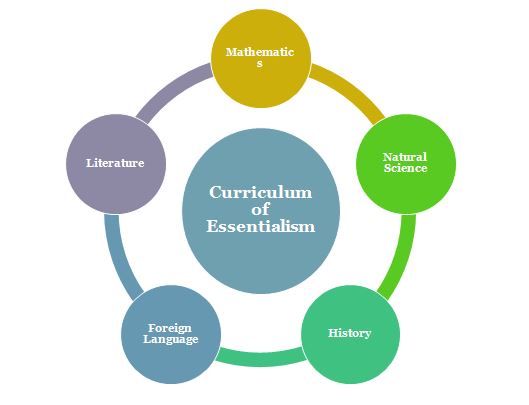
Curriculum of Essentialism
Reconstructionism
Premises of Reconstructionism
The two major premises of reconstructionism
· Society is in need of constant reconstruction or change
· Such social change involves a reconstruction of education and the use of education in reconstructing the society background.
Social Reconstructionism
Is a philosophy that emphasizes the addressing of social questions and a quest to create a better society and worldwide democracy. Typically a reconstructionist focuses on a curriculum that highlights social reform.
Background of Reconstructionism
Emphasizes the addressing of social questions. A quest to create a better society and worldwide democracy. Reconstructionist educators focus on a curriculum that highlights social reform as the aim of education.
For more details download PPT

Comments
Post a Comment
any suggestion on my side