Unit No.2
Introduction to Educational Research
u What is Research?
Research is not only a set of skills, but also a way of thinking. Within this framework of thinking and a systematic means of problem solving (Tuckman 1978)
- Systematic – research process
- Logical – induction/deduction
- Empirical – evidence based
- Reductive – generalisation
- Replicable – methodology.
Educational Research:
The application of the scientific method to study educational problems. The goal is to explain, predict, and/or control educational phenomena
Steps for conducting educational research
u Selection of a problem
u Use of specific research procedures to design and collect data
u Analysis of data
u Statement of conclusions based on the results of the data analyses
Difficulties conducting educational research
u Involves human beings and the complexities associated with them
u Difficulties generalizing from specific studies
u Problems when imposing sufficient controls to conduct research in educational settings
u Complications when observing in educational settings
u Indirect measurement of the variables being studied
Main characteristics
• Research is purposive
• Research is objective
• Research endeavors to organize data in quantitative terms
• Research usually involves hypothesis
• Research collects facts
• Emphasis on discovery of scientific generalization
• Research is unbiased
Specific Characteristics of Educational Research
u Related to the study of complex relationships of various facts.
u Employs methods of description, explanation, interpretation, sympathetic of intuitive understanding methods.
u help them to narrow down the proverbial gap between theory and practice in education.
u resulted in the findings of individuals completely similar in structure or behaviour.
u concerned directly with the problems of school.
u can properly concern itself with such matters as child development, class organization, teacher-pupil relationships interaction with the community, curriculum matters, teaching techniques, and many others.
Advantages of Educational research
u Educational research economies efforts and increases efficiency
u Brings confidence in teacher
u Bring dignity to the work of the teacher.
u Leads to adoption of new method.
u It keeps up alert
u Brings sense of awareness
u Bring better understanding of teaching learning process
u Enables to have better understanding of social life.
u promotes educational reforms.
Classifying Research
Two helpful ways to view research
u Research By Purpose
q Basic
u Basic research is mainly concerned with generalizations and the formulation of theory. It is driven by curiosity or interest in a subject. The main motivation is to expand man’s knowledge, not to create or invent something.
u research designed to test or refine theory
q Applied
u It involves practical problems of the society. It can be argued that the goal of applied research is to improve the human condition.
u research conducted in a field of common practice and concerned with the application and development of research based knowledge
q Action
u It is a unique form of applied research and a reflective process of progressive problem solving. It is also called “practitioner research” because of the involvement of the actual practitioner in real life. Action implies that the practitioner is involved in the collection of data, analysis, and the interpretation of results.
u research designed to solve a specific classroom or school problem, improve practice, or make a decision at a single local site
q Evaluation
u Evaluation as an analytical tool, involves investigating a policy program to obtain all information pertinent to the assessment of its performance, both process and result
u research designed to assess the merit and worth or a specific practice in terms of the values operating at a site
u Research by Methods
- Descriptive Research.
- Quantitative Research (Survey, Causal-comparative, Correlation)
- Qualitative Research ( Case study, Ethnography, Phenomenology, Grounded theory)
- Experimental Research.
1. Pre-experimental designs
2. True-experimental designs
3. Quasi-experimental designs
4. Factorial design
- Historical Research.(Qualitative Research)
Legal Research, Bibliography Research are the part of the Historical Research
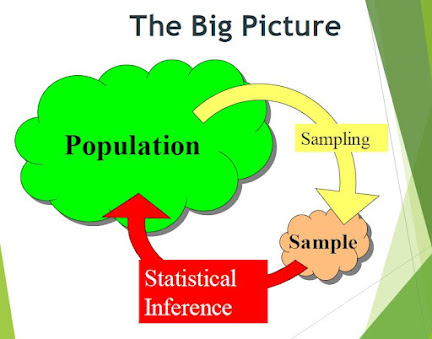
Population
A particular group of individuals or elements who are the focus of the research
Two way of Population
1. Target population: The target population is also know as the theoretical population and refers to the entire group of individuals or objects to which a researcher is interested to generalize the conclusions. This type of population usually has varying degree of characteristics.
2. Accessible population: The accessible population as the study population. It is the population to which a researcher can apply the conclusion of the study. This population is a subset of the target population.
u Sample
A sample is simply a subset or subgroup of population. Sampling is the process of selecting some individuals from the accessible population in a way that these individuals represent whole accessible population.
Sampling frame: A listing of every member of the population, using the sampling criteria to define membership in the population. Subjects are selected from the sampling frame
u Sampling plan: Outlines strategies used to obtain a sample for a study
u Probability sampling plans
u Non probability sampling plans
u Probability Sampling
u Simple random sampling : It is, in which each element of the population has an equal independent chance of being included in the sample. Thus a sample selected by randomization method is known as simple random sampling. In simple random sampling , most commonly used method is the ‘’lottery method’’.
u Stratified random sampling : The population is divided into two or more groups called strata, on the basis of some characteristics such as geographic location, age, income or status and sub samples are randomly selected from each strata.
u Systematic random sampling: It is the type of probability sampling, in which one or two items are selected randomly, but other items are selected by adding the average sampling interval to the item selected randomly. It is also called an Nth name selection technique. Selecting every nth subject from a list of the member of the population.
u Cluster random sampling: The process of randomly selecting groups, not individuals, within the define population sharing similar characteristics. Cluster are location with in which group of member of the population can be found.
u Non probability Sampling
u Convenience Sampling: it is also called accidental sampling. Weak approach to sampling because it is hard to control for bias. The sample includes whomever is available and willing to give consent. Representativeness is a concern.
u Quota Sampling: Uses convenience sampling, but with a strategy to ensure inclusion of subject types who are likely to be underrepresented in the convenience sample. Goal is to replicate the proportions of subgroups present in the population. Works better than convenience sampling to reduce bias
u Purposeful or Purposive Sampling: it is also called judgmental or selective sampling. Efforts are made to include typical or atypical subjects. Sampling is based on the researcher’s judgment.
u Network Sampling: it is also called snowball sampling. Takes advantage of social networks to get the sample. One person in the sample asks another to join the sample, and so on.
u Theoretical Sampling: Used in grounded theory research. Data are gathered from any individual or group that can provide relevant data for theory generation. The sample is saturated when the data collection is complete based on the researchers’ expectations. Diversity in the sample is encouraged.
For more details download PPT


Comments
Post a Comment
any suggestion on my side